NORFOLK, Va. — Air quality can become an issue when wildfires spark across the U.S. and Canada or when densely populated areas use a lot of fossil fuels.
Let's talk about how scientists measure air quality. The air quality index measures the amount of pollutants that are present in the air. It specifically takes into account these five pollutants:
- Aerosols - this can be dust, wildfire smoke, or volcanic ash
- Carbon monoxide
- Nitrogen dioxide
- Sulfur dioxide
- Ground-level ozone
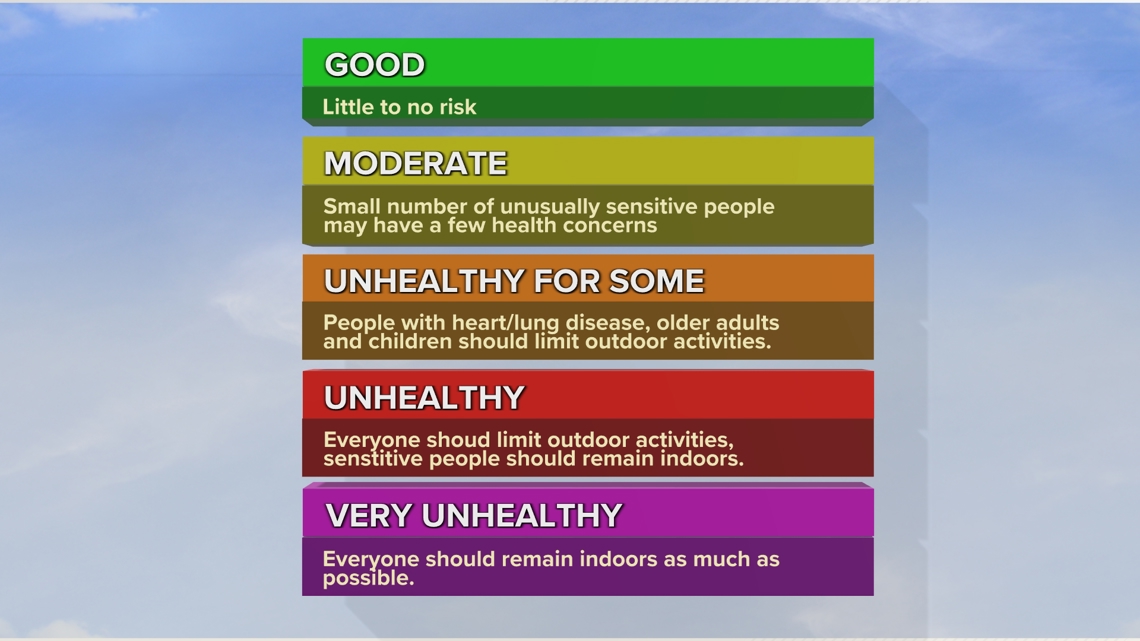
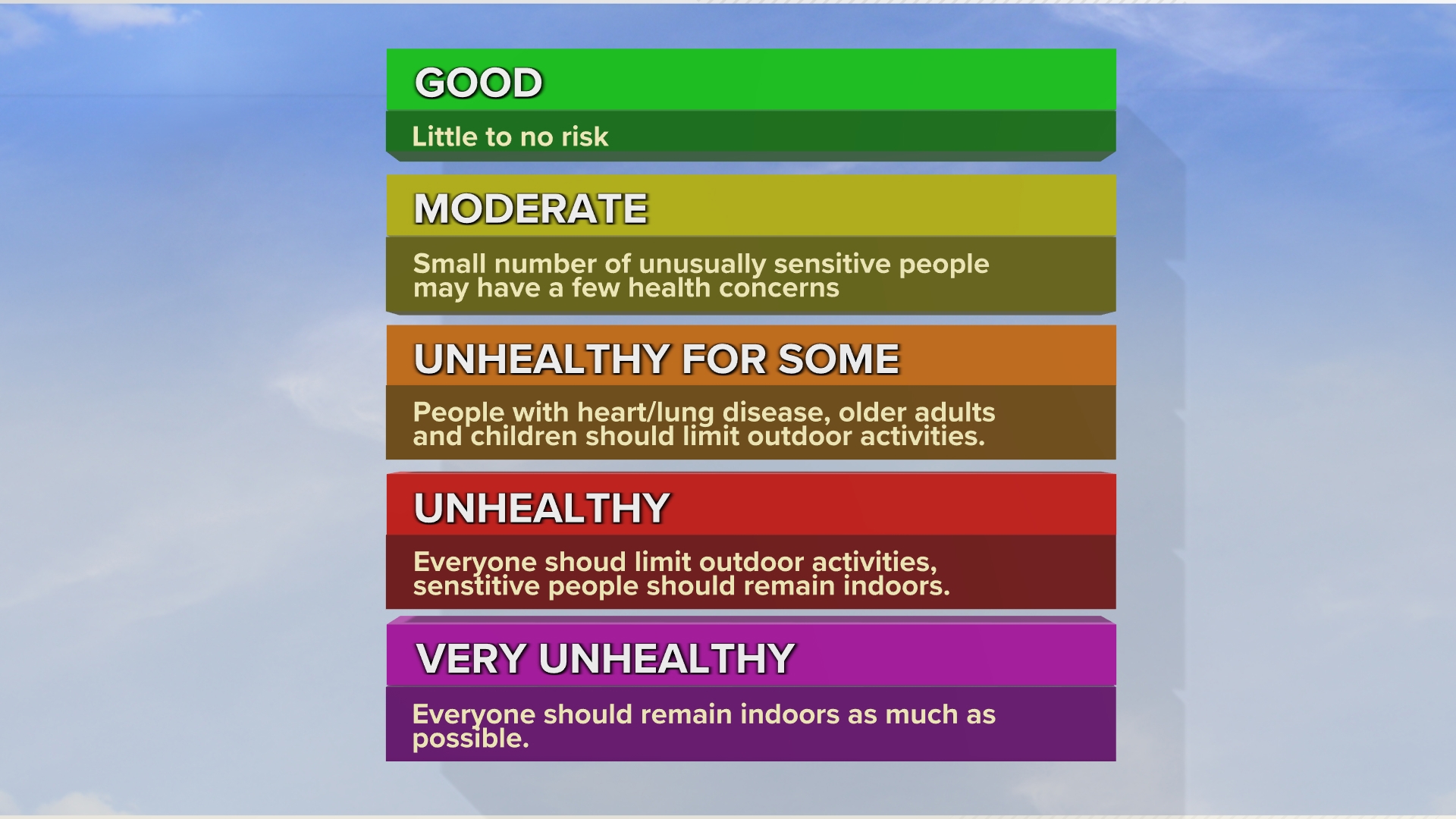
The air quality index is measured on a scale of zero to 500. The higher the number, the worse the air quality is. Any number 50 or under is considered "good" air quality.
The air quality can become worse when wildfire smoke spreads from the source of the fire to other parts of the continent. Additionally, when the sun heats the ground-level ozone, this can reduce the air quality, too.
Ground-level ozone is formed from human use of fossil fuels. Not all ozone is bad though. The ozone found in the stratosphere, the second layer of Earth's atmosphere, blocks some of the sun's harmful radiation.
Once the air quality index number rises between 51 to 100, we enter the moderate air quality level. This means that a select few citizens who are extremely sensitive to pollutants may feel some health impacts.
It's Code Orange and above where the quality of the air becomes particularly hazardous. In the Unhealthy for Some, Unhealthy, and Very Unhealthy levels, health officials suggest limiting outdoor activities.
Under these conditions, most people will have trouble breathing. People exposed to prolonged periods of poor air quality have been linked to the development of pneumonia, lung cancer, and stroke.